Farai Mabeza
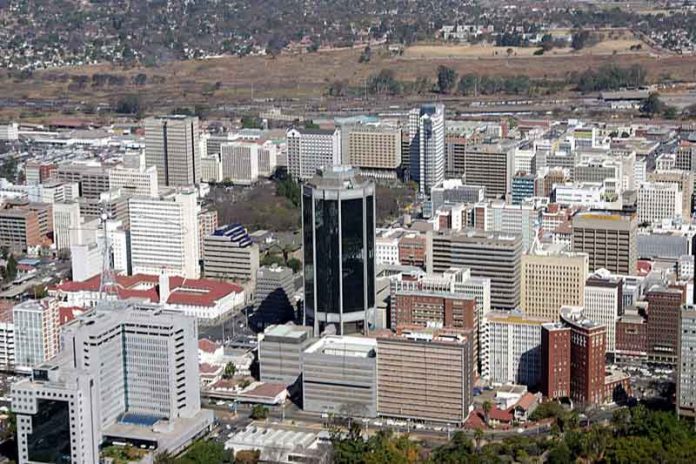
Government will set up a national productivity institute under the just launched five-year national development strategy as one of its key strategies for the productive sectors in order to spread what it termed productivity consciousness.
According to the NDS the sector growth strategies that anchor the new blueprint will be based on optimal exploitation of abundant opportunities in agriculture, mining, tourism and electricity generation.
“The Zimbabwe National Productivity Institute will be established to spearhead the promotion of productivity consciousness in all sectors of the economy,” the government said in the latest strategy.
Under the strategy for the productive sectors it is espoused that the manufacturing sector will benefit from the resuscitation and strengthening of existing value chains and development of new ones as well as mineral beneficiation.
The value chains that will be prioritised are mainly those existing in agro processing. These include the soya bean, cotton, leather and fertiliser value chains. Outside agro processing, priority will be to resuscitate the pharmaceutical and bus and trucks assembly value chains.
Regarding mineral beneficiation, the NDS1 priority is to strengthen gold processing, diamond cutting and polishing, platinum base metal refining and ferrochrome processing.
Resuscitation of value chains will be supported by scaling up of innovation hubs and industrial parks.
For the agriculture sector the authorities admitted that resolving the security of tenure on the land in order to attract investment will be crucial together with creating conditions which will create conditions for bankability of agricultural projects.
Equally important will be restructuring of Agribank into a Land Bank, and expansion of contract farming to other crops and livestock as well as strengthening existing contract farming arrangements.
Banks will be incentivised to lend to agriculture and will be persuaded to move away from the current practice where most financial institutions are investing in non-productive short term instruments.
In order to drought proof agriculture, irrigation rehabilitation and expansion, promotion and adoption of research that improves productivity of seed and animal varieties, upscaling of climate smart agriculture practises such as Pfumvudza/Intwasa, and capacitation of extension services will be prioritised.
To improve predictability in the marketing of agricultural produce, the strategy under the NDS1 will be to operationalise the commodity exchange, supported by a well-functioning regulated warehouse receipt system. تعريف القمار
In mining priority will be extended to formalisation and capacitation of the small-scale miners through the Mining Industry Loan Fund. To prevent speculative hoarding of claims across all minerals, Government plans to strengthen the enforcement of the “Use It or Lose It” principle.
Zimbabwe has hardly realised the full value of its mineral resources due to leakages in the form of transfer mispricing, smuggling and under declaration.
Zimbabwe is also underexplored.During NDS1, programmes will be undertaken to enhance exploration. The ‘Finders Keep it Principle’ will be adopted to encourage exploration. However, a time frame to utilise the findings will be adopted after which the ‘Use it or Lose Principle’ will apply.
Weak governance in the sector has also been a major limiting factor.
“In order to achieve increased and sustained growth in the mining sector, priority during the NDS1 Period will be to improve the ease of doing business in the sector. This will be realised through finalisation and implementation of mineral specific policy frameworks and a comprehensive review of the Gold Trade Act, Precious Stones Trade Act and amendment of the Mines and Minerals Act”.
The country boasts of over forty minerals including gold, platinum group metals (PGMs), diamonds, coal, gemstones, granite, manganese, chrome, lithium, asbestos, iron ore, copper, nickel, cobalt, limestone, coal-bed methane (CBM) and rare earth minerals.
In 2020 the tourism industry has been one of the worst-hit sectors by the COVID-19 pandemic after arrivals also fell by 11% in 2019 following an average growth of 6% per annum over the period 2015-2018. عدد بطولات راموس
During the planning period, the tourism sector is expected to turn around its fortunes riding on its resilience and its low hanging status as a low investment and high output sector. Enabling infrastructure developments such as the ongoing upgrading of the Beitbridge- Harare-Chirundu and the Karoi-Binga Highways among others, will widen opportunities for further tourism growth. افضل كازينو اون لاين
The growth of the tourism sector will be anchored on increased investment in diversified tourism products such as heritage tourism, medical tourism and community based tourism, among others. Key flagships will be the opening up of new tourism resorts in Kanyemba, Tugwi Mukorsi, Kariba and the development of new nodes anchored on the Victoria Falls Special Economic Zone, notably in Masuwe, Batoka, Gwayi Shangani Dam, Binga and Sijarira.
Zimbabwe continues to experience negative perceptions in key source markets and this has restricted tourism growth. This underlies the need to address country image issues and accelerate destination marketing amongst other initiatives.
This will be complemented by the operationalisation of the Tourism Support Scheme to enhance funding for the Tourism Recovery and Growth of the sector and the provision of appropriate incentives to promote foreign and local investment, especially in the Tourism Development Zones.